If you’re a serious gamer, it’s time to upgrade to a dedicated gaming monitor. Those regular old monitors you’ve been using just don’t cut it for today’s high-powered gaming PCs and consoles. Gaming monitors are designed specifically for, well, gaming, and they offer a host of benefits for gamers.
First, gaming monitors typically offer faster refresh rates, like 144Hz or even 240Hz, compared to the standard 60Hz found on regular monitors. A higher refresh rate means smoother motion with less blur. For fast-paced action games where every frame matters, a high refresh rate can give you a competitive edge. Once you experience 144Hz or faster gaming, you’ll never want to go back.
Gaming monitors also typically have lower input lag, meaning the time it takes for your inputs, like hitting a button or moving the mouse, to translate into on-screen actions is minimized. When you have to react quickly in games, those extra milliseconds of input lag on a regular monitor could spell the difference between winning and losing. Gaming monitors cut down on input lag for a very responsive gaming experience.
Many gaming monitors also support adaptive sync technologies like NVIDIA G-Sync and AMD FreeSync. These sync up your monitor’s refresh rate with the frame rate of your game for ultra-smooth, stutter-free gaming without screen tearing. Especially for fast-paced action games, adaptive sync is a must-have feature for serious gamers.
Some gaming monitors have additional features tailored to gamers like crosshair overlays for first-person shooter games, genre-specific display modes with optimized color settings, built-in timers, and more. The gaming-centric features and technologies are what set dedicated gaming monitors apart.
If you want the best visual experience for gaming with smooth performance, minimal lag or stutter, and tools built specifically for gamers, a proper gaming monitor should be at the top of your shopping list. Your PC and console games will never look or feel better than on a monitor purpose-built for gaming. In this article we are going through everything you should know about gaming monitors before buying one.
Panel
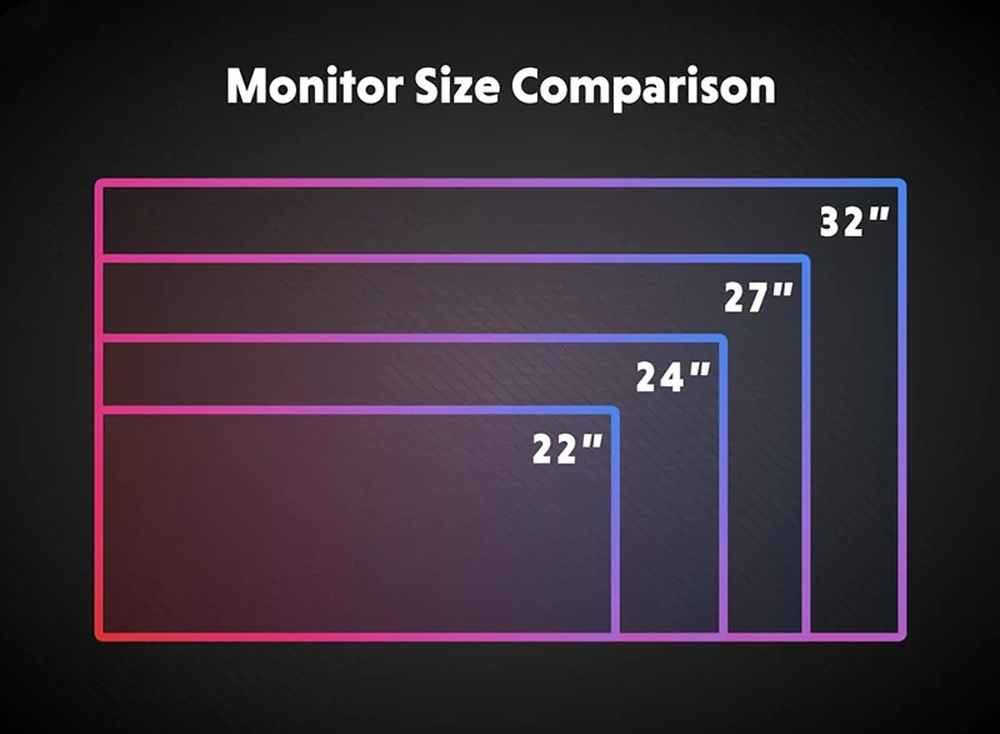
The Screen Size Battle: Which Monitor Panel Size Is Best For You?
One of the first decisions you have to make is the screen size. Monitor panel sizes range from small 24 inch screens all the way up to massive 49 inch ultrawide panels. But which size monitor is best for you? The answer depends on what you need the monitor for and how much desk space you have available. Here are the pros and cons of different monitor panel sizes to help you decide:
24-27 Inch Monitors
These are commonly referred to as “full HD” or “1440p” monitors due to their 1920×1080 or 2560×1440 resolution. 24 to 27 inch monitors are great options for general use like web browsing, office productivity, and light gaming. They are reasonably priced, have good image quality, and fit well on most standard desks. However, you will have less screen real estate compared to larger monitors.
Pros: Affordable, good image quality, easy to fit on desk
Cons: Less screen space compared to larger monitors
32-34 Inch Monitors
These “4K” monitors range from 32 to 34 inches and have screen resolutions around 3840×2160. They offer a significant upgrade in screen space and clarity over 24-27 inch panels while still fitting on most desks. 32-34 inch monitors are excellent options for productivity work involving lots of windows, multitasking, and viewing photos and videos.
Pros: Lots of screen space, sharp image clarity, great for productivity
Cons: More expensive, may require larger desk
36+ Inch Monitors
Anything bigger than 36 inches starts to get into “super ultrawide” territory. These giant monitors have an ultra-stretched aspect ratio, offering a truly immersive experience. They are amazing for multitasking, photo and video editing, and advanced gaming setups. However, they are massive in size and very expensive.
Pros: Immersive screen space, great for hardcore gamers and creators
Cons: Extremely expensive, require a huge amount of desk space

Ultrawide Monitors
Ultrawide monitors have an aspect ratio of 21:9 or wider, allowing you to fit more information across the screen without scrolling. Common sizes are 34 and 38 inches. Ultrawide monitors are perfect for creative work since you can fit a lot of art panels or rows of spreadsheet data onscreen at once. However, they do have some compatibility issues with games and apps that weren’t designed for ultrawide resolutions.
Pros: More efficient use of screen space, great for productivity and gaming
Cons: Compatibility issues, more expensive than regular monitors

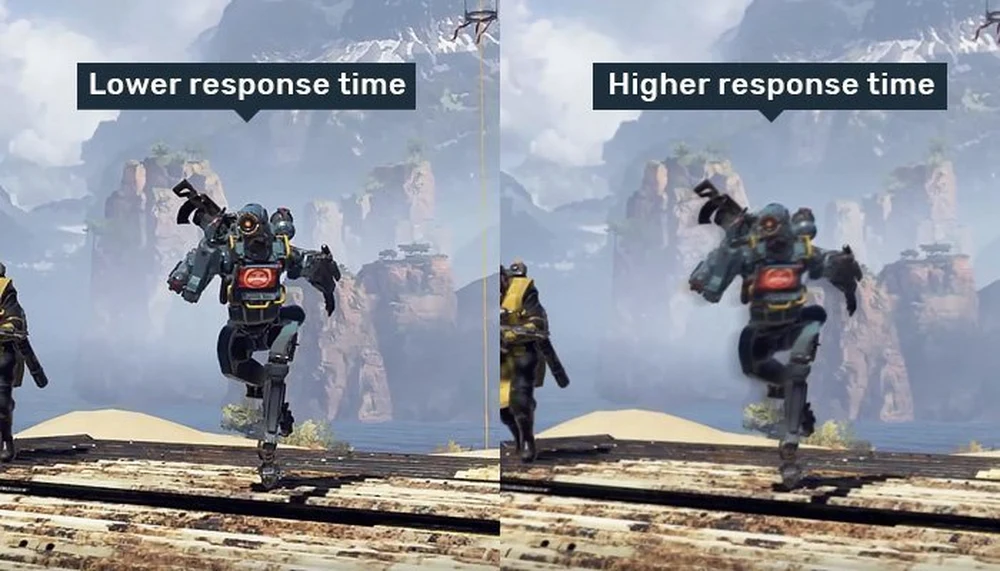
Gaming Monitor Response Times: Faster Isn’t Always Better
When buying a gaming monitor, one of the most important specs to consider is the response time. Response time refers to how quickly a monitor can change pixels from one color to another. For gaming, a faster response time means less blur and ghosting during fast-paced action. However, once you get below a certain threshold, faster is not always better. Here are the different response time options for gaming monitors and the pros and cons of each:
1ms Response Time
Monitors advertised as having a 1ms response time claim to have the absolutely fastest transitions between colors. These are usually marketed toward hardcore competitive gamers who want the least amount of blur possible. However, 1ms response times are often achieved through overdrive techniques that can cause issues like inverse ghosting and color shifting. Some 1ms monitors still exhibit noticeable blur in practice.
Pros: Theoretically the least amount of blur
Cons: Can suffer from overshoot issues, not always noticeably faster than 4-5ms

4-5ms Response Time
Most mid-range gaming monitors have response times between 4 and 5ms. These panels provide very fast response without the downsides of many 1ms displays. For most gamers, the difference between 1ms and 4-5ms monitors is negligible in actual use. 4-5ms panels provide a good blend of speed, image quality, and cost effectiveness.
Pros: Good balance of speed and image quality
Cons: Slightly more blur than 1ms
8-10ms Response Time
Monitors with 8-10ms response times are noticeably slower and are not recommended for serious gaming. They are often aimed more at general productivity use and casual gaming. While they are cheaper, 8-10ms monitors will exhibit significant ghosting during fast-paced shooters and racing games.
Pros: Inexpensive
Cons: Significant ghosting during gaming
In reality, advertised response times often don’t match a monitor’s true performance. Many factors like overdrive settings, panel technology, and overall image processing influence perceived response. Monitors with similar response times can perform very differently in practice.
The most important thing is to read reviews from trusted sources and watch actual gaming footage to determine a monitor’s real-world performance. For most gamers, a 4-5ms panel from a reputable manufacturer will provide great speed without issues, for a reasonable cost. Only competitive esports gamers likely need the absolute fastest 1ms panels. Focus more on other specs like resolution, refresh rate, and input lag that also impact gaming performance.
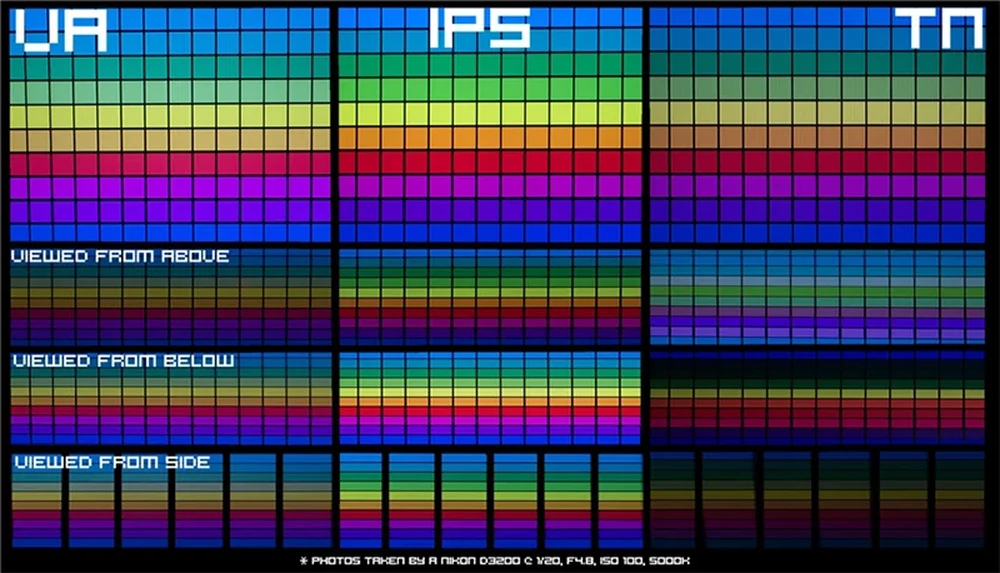
Which Gaming Monitor Panel Type Is Best? TN, VA, IPS Explained
The panel type can have a big impact on performance and image quality. The three main panel types used in modern gaming monitors are TN, VA and IPS. Each offers different strengths and weaknesses, so choosing the right type for your needs can make a big difference.
TN Panels
Twisted Nematic (TN) panels are the most common and budget-friendly options for gaming monitors. They offer the fastest response times (1-2ms) and highest refresh rates, making them a popular choice for esports gaming. However, TN panels suffer from limited viewing angles and less vibrant colors compared to IPS and VA displays.
Pros: Fastest response times, high refresh rates, inexpensive
Cons: Narrow viewing angles, dimmer colors
VA Panels
Vertical Alignment (VA) panels provide better contrast ratios, darker blacks and more vibrant colors than TN screens. Response times for VA monitors have also improved significantly in recent years. However, VA technology still lags slightly behind TN panels in terms of sheer speed. VA panels also commonly suffer from slight color shift when viewed off-angle.
Pros: Deeper blacks, better contrast, vibrant colors
Cons: Slower response times, potential for color shifting
IPS Panels
In-Plane Switching (IPS) panels are known for their wide viewing angles, accurate colors and rich detail. They are the preferred choice for professionals who work with color-critical content like photos and videos. However, traditional IPS panels have slower response times versus TN and VA technologies, which can cause issues with motion blur during fast-paced gaming. Newer “IPS-like” panels have closed this performance gap to some extent.
Pros: Very wide viewing angles, accurate colors
Cons: Slower response times, more expensive
For gaming, TN panels provide the absolute fastest performance but sacrifice some color and viewing angle quality. VA panels offer a decent balance of speed, color and contrast while IPS screens prioritize color accuracy over pure speed. Consider the types of games you play and what aspects of image quality matter most to you.
For esports and competitive gaming, a high-refresh TN monitor will provide the least input lag and motion blur. But for single-player gaming, an IPS or high-end VA display with wider colors and deeper contrast may create a more immersive gaming experience. While panel type does impact performance, features like resolution, refresh rate and response time also factor into an overall gaming experience. Do your research, assess your priorities and choose the monitor panel that best caters to your specific gaming needs.
Gaming Monitor Backlights: LED, OLED, Mini LED Explained
The backlight is one of the most important factors that determines how good your gaming monitor looks. Different backlight technologies offer varying benefits in terms of brightness, contrast, image quality, and power efficiency – all of which affect your gaming experience.
The three main types of backlights used in monitors today are LED, OLED and mini LED. Here’s what you need to know about each option for a superior gaming display:
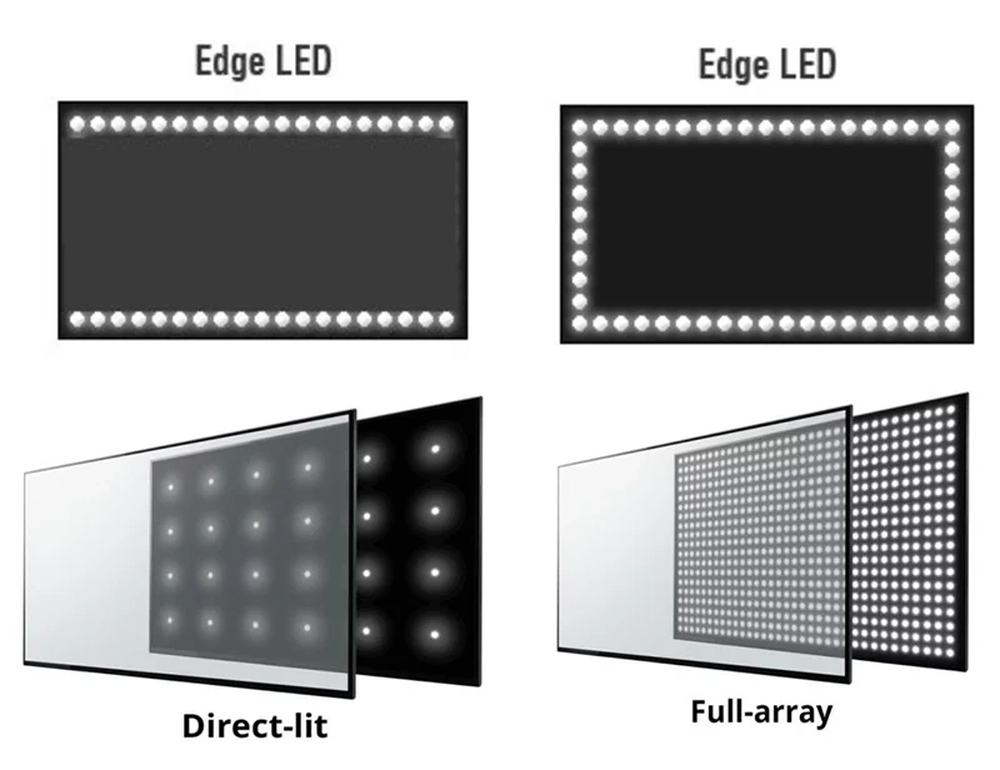
LED Backlights
Traditional LED backlit monitors have an array of individually-controlled LEDs located around the edge of the screen that cast light through the panel. This ‘edge lit’ design provides benefits like high brightness, deep blacks and consistent color accuracy. However, LED monitors have limitations in terms of contrast ratio, local dimming capabilities and viewing angles compared to OLED and mini LED displays.
Pros: High peak brightness, inexpensive
Cons: Limited contrast, narrow viewing angles
OLED Backlights
OLED (organic light emitting diode) stands out for its perfect blacks, infinite contrast ratio and wide viewing angles. Since each pixel produces its own light, OLED monitors can achieve extreme levels of image depth, vibrancy and detail. However, OLED screens suffer from potential burn-in issues when displaying static images for long periods. They also lack the high peak brightness of LED and mini LED panels.
Pros: Infinite contrast ratio, perfect blacks, wide viewing angles
Cons: Potential for burn-in, limited brightness
Mini LED Backlights
Mini LED features thousands of tiny LEDs arranged in ‘local dimming zones’ across the screen, rather than just along the edges. This allows for much finer light control and higher contrast ratios compared to traditional LED panels. Mini LED monitors also offer higher peak brightness, wider color gamut and better HDR performance. However, mini LED displays tend to be more expensive than standard LED monitors.
Pros: Higher contrast ratios, added local dimming
Cons: More expensive, less widespread
For gaming, each backlight type offers advantages and trade-offs. OLED monitors provide the deepest blacks, most lifelike images and a true HDR experience. But they’re expensive and prone to burn-in. Mini LED panels hit a good balance between contrast, HDR and brightness – ideally suited for HDR gaming. Standard LED monitors are cheaper and brighter but lack the contrast and local dimming of OLED/mini LED screens.

Flicker Free Gaming Monitors: Why They Matter
You may see the term “flicker free” thrown around. But what does that actually mean, and why should you care? Flicker occurs when a monitor’s backlight rapidly turns on and off, causing an unnatural strobing effect that can irritate your eyes over time. While minor flicker may go unnoticed, serious flicker can lead to headaches, eyestrain and blurred vision.
Flicker-free monitors have special technologies that eliminate or drastically reduce backlight flickering, providing a more comfortable viewing experience. This is especially important for tasks that involve long periods of screen time like gaming and productivity work.
Why do monitors flicker? Traditional LCD monitors use some form of backlight modulation – often with cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFL) – that rapidly adjusts the screen’s brightness to reproduce an image. This pulsating brightness creates the flickering effect that some people can perceive.
To eliminate flicker, modern monitors utilize flicker-free technologies like:
• LED Backlights: Light emitting diodes (LEDs) provide more consistent illumination compared to CCFL and reduce unwanted flickering.
• Constant Voltage: The monitor’s voltage regulator maintains an even voltage output to prevent current fluctuations that cause flicker.
• Overdrive Circuits: Specialized circuits compensate for changes in brightness between frames, smoothing out transitions that can produce flicker.
For gaming, a flicker free monitor provides less visual strain during long sessions – potentially improving your performance, concentration and comfort. While most premium gaming displays now feature flicker free technologies, check customer reviews to confirm a monitor’s actual flicker levels before purchasing.

How Bright Should Your Gaming Monitor Be?
When choosing a gaming monitor, brightness is an important factor to consider. But how bright is bright enough for optimal gaming?
Most standard LCD monitors have a brightness range between 200 and 350 nits. These displays are suitable for indoor use in typical lighting conditions. However, for demanding gaming sessions – especially in well-lit rooms – you’ll likely want a brighter monitor.
Brighter gaming monitors in the 400 to 600 nit range offer several benefits:
Visibility – Higher brightness levels improves the visibility and clarity of on-screen objects and text, making it easier to see enemies and details in fast-paced games.
Glare Reduction – Extra brightness helps compensate for reflections from overhead lights and windows, maintaining better image contrast even in lit rooms.
HDR Support – Gaming monitors with brightness over 1,000 nits are required for full high dynamic range (HDR) compliance. HDR delivers deeper contrast, wider colors and more realistic lighting effects in compatible games.
Eye Strain – Studies have shown that adequate screen brightness can help reduce eyestrain compared to dim displays, leading to more comfortable long gaming sessions.
While very bright monitors above 1,000 nits are ideal for HDR gaming, 500 to 700 nits of brightness should be sufficient for standard gaming in lit environments without HDR.
Performance

Gaming Monitor Refresh Rates: Why Hertz Matters For Gamers
One of the most important specs to consider is the refresh rate, measured in hertz (Hz). The refresh rate determines how smoothly fast-paced action will appear onscreen by controlling how many times per second the monitor refreshes the image. For gamers, a higher refresh rate monitor can significantly improve responsiveness, reduce input lag and minimize motion blur. Here are the main refresh rate options and their impact on gaming:
60Hz Refresh Rate
The standard 60Hz refresh rate has been the norm for computer monitors for decades. At 60Hz, the monitor refreshes the image 60 times per second. While 60Hz works reasonably well for most productivity tasks, it is barely sufficient for gaming and can result in noticeable lag, blur and stutter during fast action. However, 60Hz monitors are still common options due to their low cost.
Pros: Inexpensive
Cons: Noticeable input lag and motion blur
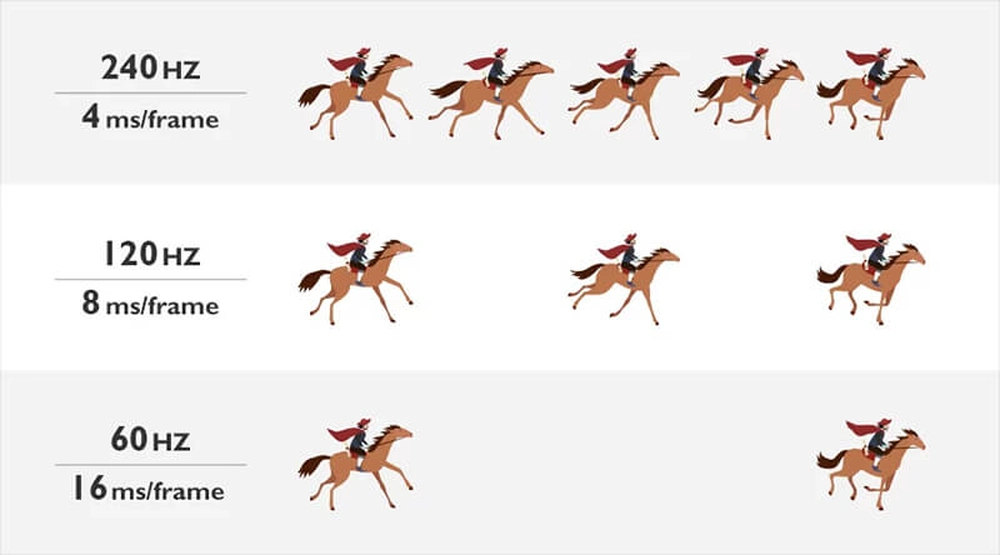

144Hz – 240Hz Refresh Rate
Gaming monitors with refresh rates of 120Hz or higherare considered “high refresh rate” displays. At these speeds, the monitor refreshes the image well over 100 times per second, significantly reducing input lag and motion blur compared to 60Hz screens. For competitive gamers and those sensitive to lag, 120Hz or higher is ideal. 240Hz is the current pinnacle, though the difference from 144Hz is minor for most people. High refresh rate monitors also require a powerful graphics card to hit frame rates above 100 fps.
Pros: Greatly reduced input lag and blur
Cons: More expensive, require high-end GPU
360Hz+ Refresh Rate
The absolute highest refresh rate gaming monitors currently go up to 360Hz or beyond. These panels are targeted at hardcore esports athletes who need literally every millisecond of information and responsiveness. While 360Hz monitors are impressive technological feats, the vast majority of people would be unable to discern any real-world difference above 240Hz. 360Hz panels require monster graphics cards and are extremely costly.
Pros: The absolute lowest input lag and blur
Cons: Nearly impossible to perceive benefits for most people, extremely expensive
For gaming, higher refresh rate monitors provide a clear and tangible benefit in responsiveness, blur reduction and visual smoothness. While 60Hz works for many, 120Hz or higher is ideal for serious gaming. Consider your budget, gaming priorities and hardware when choosing a monitor refresh rate:
• Casual gamers: 60Hz is fine but look for 75Hz or higher if possible
• Most gamers: Aim for at least 120Hz-144Hz for noticeably better performance
• Esports athletes: 240Hz offers the best performance, 360Hz is overkill for nearly all
What Is Adaptive Sync for Gaming Monitors? Benefits Explained
If you’re shopping for a gaming monitor, you’ve likely come across the term “adaptive sync.” Technologies like Nvidia G-Sync and AMD FreeSync are examples of adaptive sync, which aims to eliminate screen tearing and stuttering during gameplay. Here’s what adaptive sync is and why it matters for gamers:
By default, a monitor refreshes the image at a fixed rate (the refresh rate). For example, a 144 Hz monitor updates 144 times per second. However, graphics cards generate new frames as fast as they can, which is usually not an exact multiple of the monitor’s refresh rate.
This mismatch in frame rates between the GPU and monitor can causescreen tearing and stuttering artifacts as part of one frame gets displayed alongside part of the next frame. The result is a uneven, jarring gaming experience.
With adaptive sync, the monitor’s refresh rate dynamically adjusts to match the graphics card’s constantly changing frame rate. Essentially, the monitor refreshes the screen whenever a new frame is ready from the GPU. This syncing of refresh rates eliminates screen tearing and prevents frame pacing issues that cause stuttering and judder.
Adaptive sync technologies like G-Sync and FreeSync provide several clear benefits for PC gamers:
• Smoother Gameplay – By syncing the monitor and GPU frame rates, adaptive sync delivers a much smoother, more fluid experience free of stutters and tears.
• No Input Lag – Since the monitor refresh rates sync in real time, there is no perceptible input lag introduced by adaptive sync.
• Wider Dynamic Range – Monitors with a wide adaptive sync dynamic range can adjust their refresh rate over a bigger frequency span, for better compatibility with fluctuating frame rates.

G-Sync
Nvidia’s G-Sync uses a dedicated G-Sync module inside compatible monitors to synchronize the refresh rate with Nvidia graphics cards in real time. This provides an extremely precise and adaptive match between frame rate and refresh rate.
However, G-Sync monitors tend to be more expensive due to the custom module and are only compatible with Nvidia GPUs.
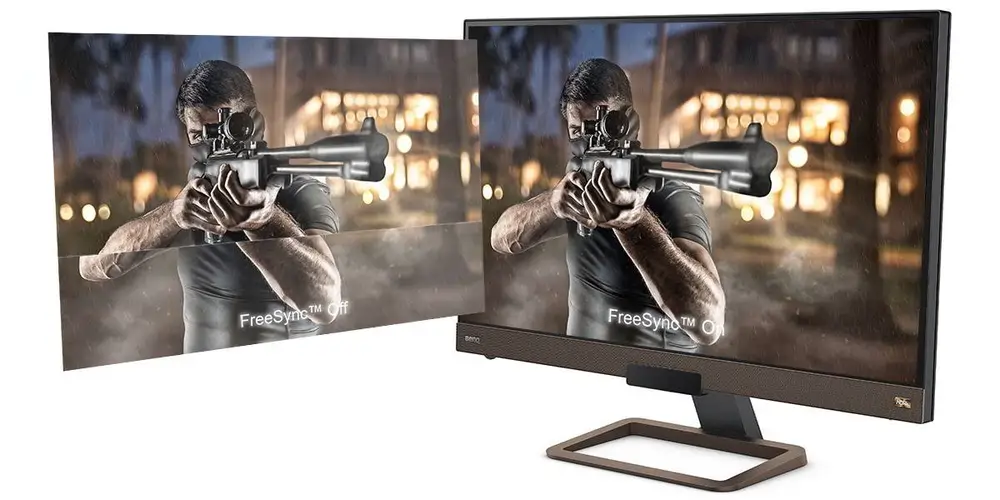

FreeSync
AMD’s FreeSync relies on the monitor’s standard display circuitry to dynamically alter the refresh rate. Since no special module is needed, FreeSync monitors are usually more affordable.
However, because FreeSync lacks a dedicated module, it relies more on the monitor’s quality of implementation for optimized performance. And FreeSync is only compatible with AMD graphics cards.

ULMB For Gaming: What Is Ultra Low Motion Blur?
You may come across the feature “ULMB,” which stands for Ultra Low Motion Blur. ULMB aims to reduce ghosting and blur during fast-paced gameplay by controlling how the monitor’s backlight illuminates the pixels. But is ULMB worth having for a better gaming experience? Here’s what you need to know:
What Is ULMB And How Does It Work?
With ULMB enabled, the monitor’s backlight will quickly pulse in sync with the refresh rate. For example, on a 120Hz monitor the backlight will flash 120 times per second. This “strobe” effect freezes the image during each refresh, preventing individual pixels from staying illuminated long enough to produce motion blur. The result is a clearer, sharper picture during fast motion.

The main benefit of ULMB is a significant reduction in perceived ghosting and motion blur while gaming, resulting in more detail and less visual distortion. This can improve performance for fast-paced first person shooters and racing games that rely on quick twitch reactions.
However, ULMB comes with some trade-offs like lower peak brightness and a global decrease in image contrast. ULMB also requires users to lower the monitor’s refresh rate, which may impact responsiveness.
What Is Monitor Overdrive And Why Do Gamers Need It?
Monitor overdrive refers to a feature that helps pixels transition between colors more quickly, reducing blur during fast motion. Here’s what you need to know about overdrive and why it matters for gamers:
Why Pixels Are Slow
Without overdrive, monitor pixels are inherently slow to transition from one color to the next. This latency can cause blur and ghosting effects when the image contains a lot of quick motion, like during gameplay. The longer it takes pixels to change, the more blurred fast-moving objects will appear onscreen.
How Overdrive Works
Monitor overdrive speeds up pixel transitions by applying an extra voltage boost as pixels change colors. This helps pixels “overshoot” their final color value and then quickly settle into the correct state. Though somewhat counterintuitive, overdriving pixels in this way can reduce their effective response time and associated motion blur.
Benefits For Gamers
The primary benefit of monitor overdrive is reduced ghosting and motion blur during gaming, resulting in a clearer image and sharper display of fast-paced action. This can enhance targeting and reactions in first-person shooters, racing games and other fast-moving titles.
Quality
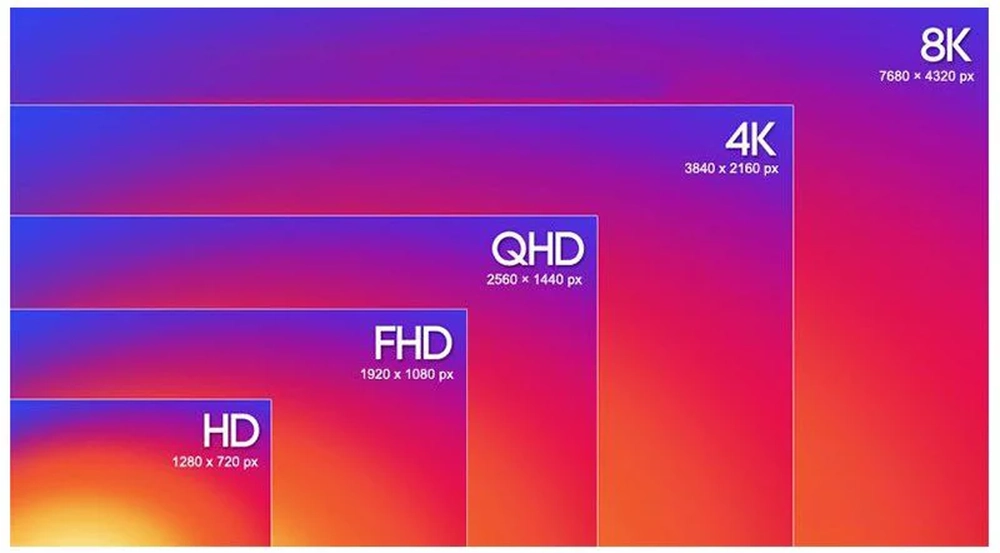
Choosing A Gaming Monitor Resolution: HD, QHD, 4K And Beyond
The resolution of your gaming monitor determines how sharp, detailed and crisp the image will appear onscreen. Higher resolutions allow you to fit more information and see finer in-game textures and details. However, higher resolutions also require more processing power from your graphics card. Here are the main resolution options for gaming monitors and which may be best for you:
HD (1080p)
The most common gaming monitor resolution is Full HD or 1080p, with a 1920 x 1080 pixel resolution. Monitors at this resolution provide a good balance of affordability, performance and image quality. While not as sharp as higher resolutions, 1080p screens are still suitable for gaming on monitors up to 27 inches. Most GPUs can easily push well over 60 frames per second at 1080p, even on intensive titles.
Pros: Inexpensive, good performance
Cons: Not as detailed as higher resolutions
QHD (1440p)
Quad HD or 1440p monitors have a 2560 x 1440 resolution, representing a roughly 40% increase in pixels over 1080p. Images and text appear noticeably sharper and clearer at 1440p. QHD gaming monitors between 27 and 32 inches provide an immersive experience with good pixel density. However, 1440p resolution demands a fair amount of processing power from high to mid-range graphics cards to achieve smooth frame rates.
Pros: Much sharper detail, more immersive
Cons: Higher GPU requirements
4K (2160p)
4K or 2160p monitors with 3840 x 2160 resolution offer the most detail and visibility thanks to an almost fourfold increase in pixels over 1080p. Text and fine game graphics are crisp and distinct at 27 inches or larger. However, pushing 4K resolution requires massive processing power from high-end graphics cards and results in lower frame rates even on reduced settings. 4K monitors also tend to be more expensive.
Pros: Absolutely sharp detail
Cons: Extreme GPU demands, higher cost
For gaming, here are the ideal resolutions for different use cases:
• Budget gamers: 1080p is still a sweet spot, providing good performance at an affordable price.
• Mainstream gamers: 1440p offers a notable upgrade in sharpness and immersion for a moderate performance cost.
• Power users: 4K delivers the ultimate immersive experience, though only high-end PCs can push consistent high frame rates at this resolution.

HDR Monitors For Gaming: What You Need To Know
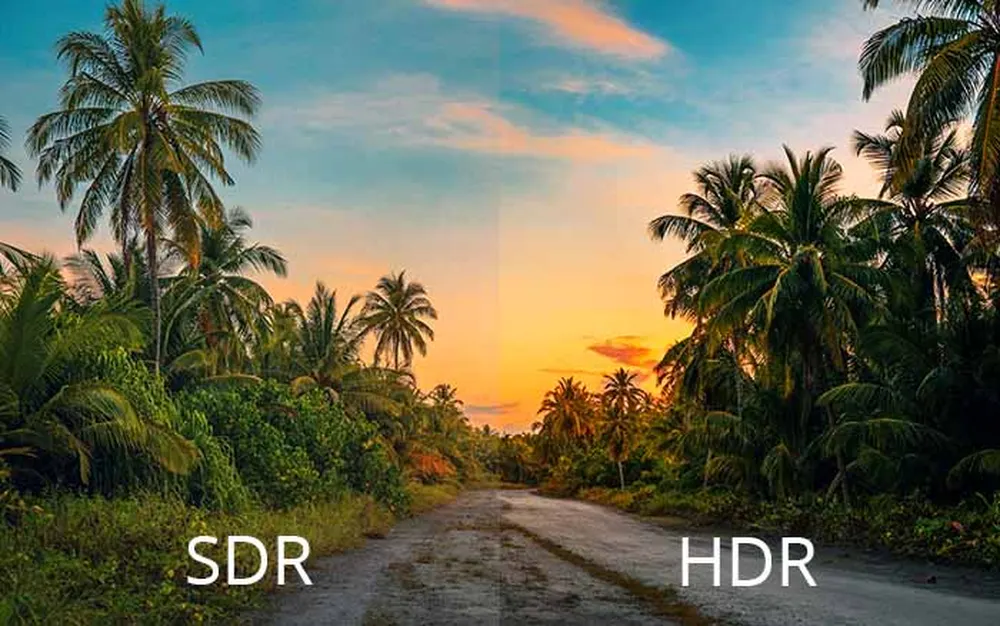
High dynamic range, or HDR, has quickly become an essential feature for top-tier gaming displays. HDR enables monitors to produce a much wider range of brightness levels and colors, resulting in more realistic and immersive visuals during gameplay. However, not all HDR monitors are created equal, and HDR support requires other components to unlock its full benefits. Here’s what you need to know about HDR gaming monitors:
What Is HDR?
Traditional monitors are limited to around 100-200 nits of brightness and around 90-100% of the sRGB color space. HDR monitors offer 1,000+ nits of brightness, support for the DCI-P3 color gamut and other capabilities to produce an image with a much wider “dynamic range” of contrast between the darkest blacks and brightest whites. This expanded color volume results in more realistic and life-like imagery.

Types Of HDR Support
There are several levels of HDR support for monitors:
• HDR 400: Around 400 nits of brightness, limited HDR capabilities
• HDR 600: At least 600 nits, more vivid HDR performance
• HDR 1000: Over 1,000 nits for full HDR image with wide color
• VESA DisplayHDR certified: Verified by the VESA HDR standard
Benefits For Gamers
When implemented properly, HDR gaming monitors can deliver:
• More Realistic Graphics: HDR produces lighting, reflections and shadows closer to real life, creating a more immersive experience.
• Wider Color Range: The expanded color gamut allows for more vivid, distinctive hues that highlight details and textures in games.
• Improved Contrast: The higher contrast ratio between dark and bright areas reveals details that might otherwise be lost.
• Compatible Game Support: Only games with HDR support can take full advantage of an HDR monitor’s capabilities.
Requirements For HDR Gaming
To fully utilize HDR, you’ll need:
• An HDR-capable gaming monitor
• A high-end GPU that can output HDR signals
• An HDR compatible video cable (DisplayPort or HDMI 2.0/2.1)
• Games that support HDR visuals

sRGB and Adobe RGB
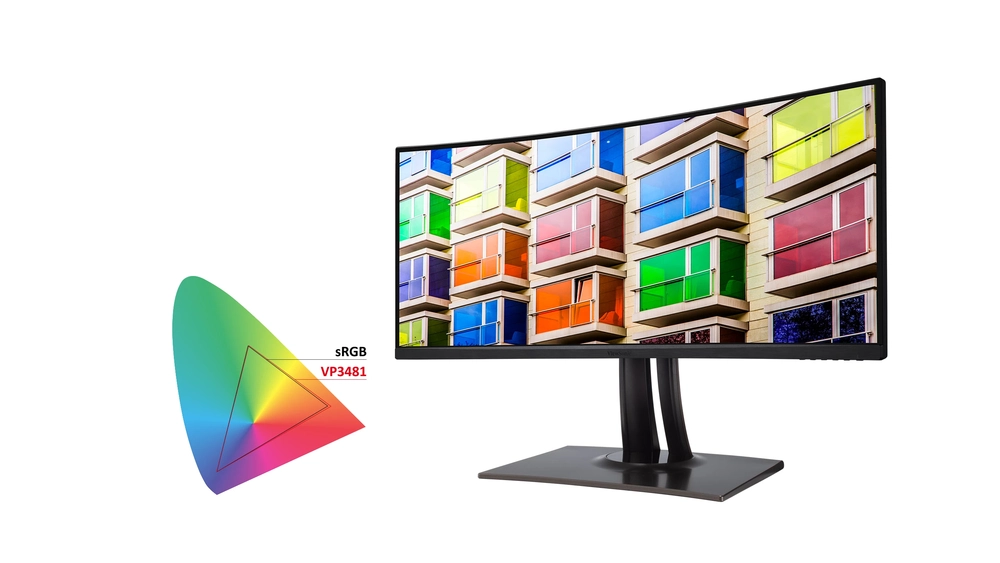
The color gamut of a monitor describes the range of colors it can produce. For gamers, a wider color gamut can enable more vibrant, realistic visuals and finer color detail in games. However, not all content supports broader color spaces. The two main color gamuts for computer monitors are sRGB and Adobe RGB. Here’s what each offers for gaming:
What Is sRGB?
The sRGB color space has been the standard for computer and web displays for years. It covers around 36% of the colors visible to the human eye. sRGB provides an accurate color representation for internet content, photos taken with most consumer cameras, and most games. Most PC monitors support the sRGB gamut natively.
Pros: Accurate color for most games and content
Cons: Limited, narrow color space
What Is Adobe RGB?
The Adobe RGB color space covers roughly 50% of visible colors, significantly wider than sRGB. It was developed for professional photographers and graphic designers seeking broader color representation for image editing. While Adobe RGB encompasses nearly all of sRGB, very few monitors, devices and content are optimized for its larger gamut.
Pros: Wider color range for more vivid hues
Cons: Limited content and device support
For most gaming use cases, an sRGB-calibrated monitor provides the ideal color accuracy. Since the vast majority of games are mastered within the sRGB color space, they will display most accurately on an sRGB-native monitor.
While an Adobe RGB monitor can technically show more vibrant, saturated colors, games would have to specifically support the wider gamut for those colors to display correctly. In practice, very few games currently take advantage of Adobe RGB.
Most gamers recommend at least 144Hz or higher refresh rate for a gaming monitor. The higher the refresh rate, the smoother fast-moving action will appear on screen. 144Hz is a good sweet spot for price and performance. 240Hz is for the most competitive gamers.
It depends on the size of your monitor and your graphics card. For 24-27 inch monitors, 1080p is still plenty sharp. For larger monitors, 1440p has more pixel density and clarity. More demanding games will require a higher-end graphics card to run at 1440p comfortably.
IPS panels have better picture quality with more vibrant colors and wider viewing angles. But they are slightly slower. TN panels are cheaper, have faster response times, but more restricted viewing angles and duller colors. For gaming, a TN panel may be preferred due to the faster response time.